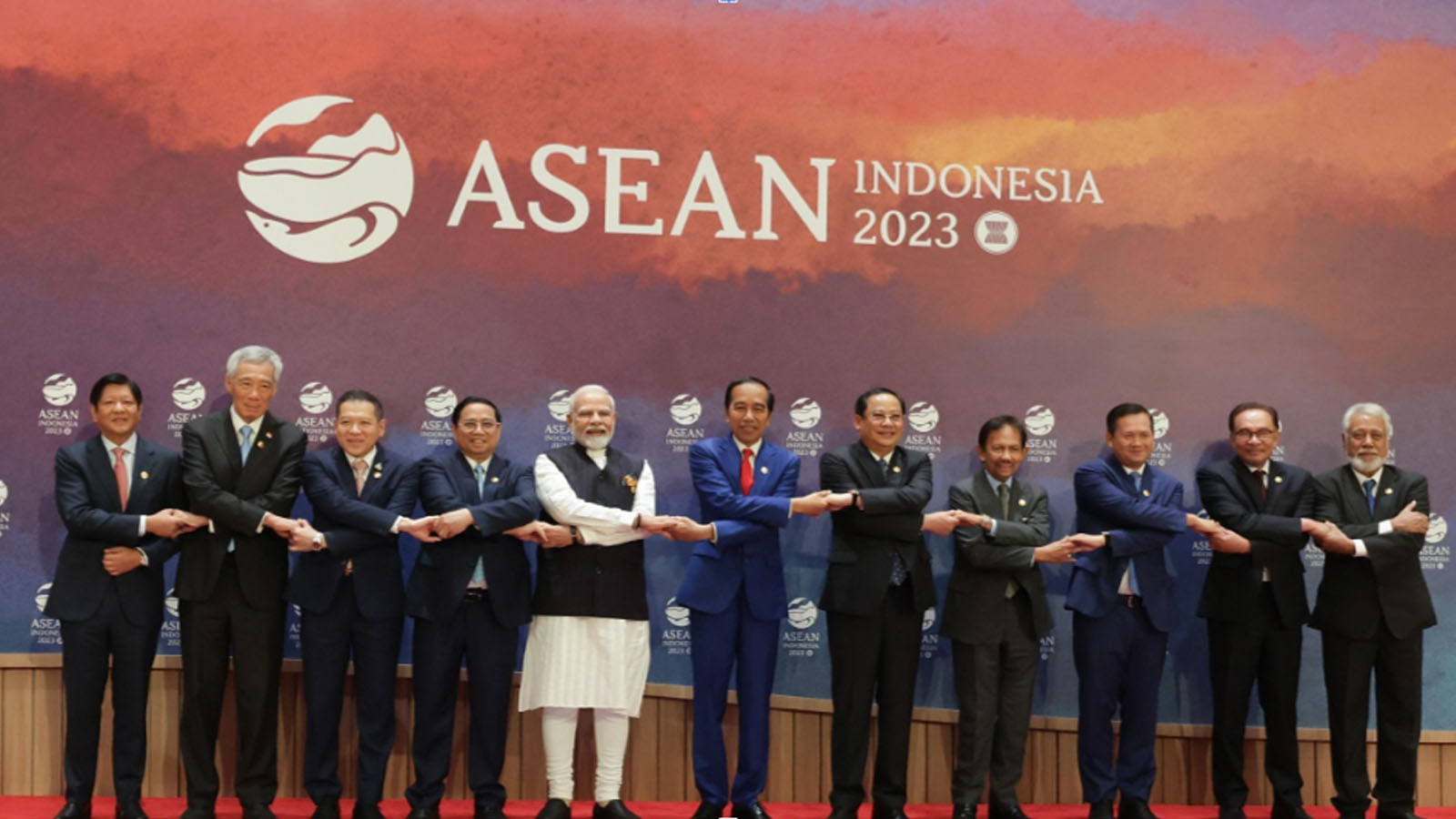
What is Act East Policy: India’s Act East Policy is a diplomatic initiative with focus on the extended neighborhood in Asia-Pacific region to strengthen economic and strategic ties. The Act East policy signifies a proactive approach to engage more deeply with the region, encompassing political, economic, and cultural dimensions. It was first announced by Prime Minister Modi in 2014 in the ASEAN Summit in Myanmar. This policy builds on the earlier Look East Policy enhancing partnerships in trade, investment, security and connectivity. The primary objectives of the Act East Policy are to enhance economic cooperation, improve strategic and security ties, institutional engagement and foster cultural and people to people contacts with countries in the Asia-Pacific region through continuous engagement at bilateral, regional, and multilateral levels. One of the priorities of the Act East Policy is to provide interface between North Eastern states of India including the state of Arunachal Pradesh and ASEAN region through trade, culture, people to people contacts and physical infrastructure- road, airport, power and telecommunications. Some of the major projects carried out under the policy include India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway Project, Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit and Transport Project, Rhi-Tiddim Road Project and Border Haats. By fostering closer ties with Eastern nations, India seeks to boost economic growth, ensure regional stability, and counterbalance China’s influence in the region. LOOK EAST TO ACT EAST : India’s Act East Policy represents a proactive evolution of the earlier Look East Policy established in 1991. The Look East Policy, Initiated under Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha emerged in the wake of significant global changes, including the end of the Cold War and the disintegration of the Soviet Union, which necessitated new economic partnerships and diversified geopolitical alignments for India. The policy’s inception aligned with India’s economic liberalization, aiming to integrate the country more deeply into the global economy by fostering ties with the economically dynamic and strategically important Southeast Asian region. The Look East Policy evolved through distinct phases. The first phase (1991-2002) concentrated on renewing political contacts, increasing economic integration, and establishing institutional linkages with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). During this……
Login to continue reading for FREE!